When Do Bed Bugs Bite and How Can They Be Treated?
When do bedbugs bite and how can they be treated? The first step is to wash the affected area with soap and water to remove any debris. Additional measures include applying a cold compress or over-the-counter anti-itch creams. Young children can also be treated by applying low-strength steroid creams. Infants’ nails should be clipped to prevent scratching. In severe cases, systemic medications, such as intramuscular epinephrine, antihistamines, or corticosteroids, may be required.
The presence of bedbugs can be very stressful. The constant itching and constant biting of the insects are often enough to prevent people from getting a good night’s sleep. Sleep deprivation can even lead to heart disease, impaired thinking, and accidents. Additionally, stress caused by an infestation can affect family relationships and work performance.
When bedbugs bite, it can result in welts, red bumps, and severe itching. While most people do not experience these symptoms, others may have a reaction lasting up to a week. In addition to the unpleasant itchiness, bedbug bites can cause emotional anxiety or depression. It is important to clean any bite site after bedbugs appear and apply a steroidal anti-itch cream with cortisone or hydrocortisone. You may also want to apply a topical anesthetic such as diphenhydramine.
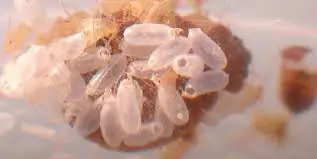
Bedbugs are wingless, small insects that live in a bed and feed on the blood of a host. The adult bed bug will lay three or four eggs a day and can lay hundreds in its lifetime. The eggs will hatch within six to 17 days. The bugs are active during the night and are often not visible during the day.