How Do Lice Turn Into Bed Bugs?
Bed bugs are not related to lice and can cause a large infestation if left unchecked for too long. Lice live on the scalp and other hair of humans. They are easily spread by contact and can even find their way inside your clothing or belongings. When they find a new hiding place, they will lay eggs in the new harborage. Unlike bed bugs, lice do not feed on people, so they are difficult to spot.
Lice and bed bugs look similar, and both can cause itchiness and irritation on the skin. However, treatment is different. Bed bugs live in bed frames and mattresses and transmit from person to person through clothing, luggage, and used furniture. If you suspect you have bed bugs, you should contact a professional pest controller for treatment. Alternatively, you can use a pharmacist’s shampoo to get rid of the bugs.
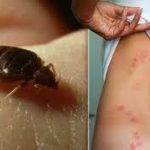
Bedbugs feed at night, usually on sleeping humans. The bites are often painless at first, but later turn into itchy welts. You can find bedbug bites on any exposed skin, including your bed. Although bedbug bites are painful, they do not transmit disease. The bites are annoying and may cause you to scratch excessively. This will disturb your sleep and possibly lead to secondary skin infections. If the itching is severe or causes you to become allergic to the bug saliva, you may need to visit a doctor.
The eggs of a female body louse mature seven days after hatching. During this time, she lives for four weeks and lays eight eggs daily. During this time, she lives inside clothing and feeds on the blood of her host. Its claws allow the louse to move through clothes and move against skin. They feed on the skin of the host and then die if there is no more blood available.