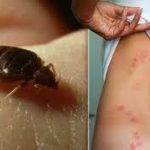
Can Bed Bugs Develop on Their Own?
Bedbugs are extremely resistant to many of the methods available to eliminate them. They are more of a nuisance than a health threat, and research has failed to prove any link between human disease and bedbugs. However, their presence does pose the risk of secondary bacterial infections that occur when the bedbugs scratch human skin.
The bites of bedbugs are generally painless when the insects first attack. However, over time, an individual may develop an allergic reaction to the bug’s saliva. This can result in red, swollen bites. The bites also tend to occur in clusters and patterns.
Bedbugs are most common in homes, but they can also be found in cars, buses, and hotels. The most common places where bedbugs live include headboards and wall-mounted beds. They are most common in single-family homes, but they can also be found in offices, colleges, hospitals, and daycare centers.
Bedbugs feed on human blood, so they must have regular meals to survive. Female bedbugs lay between two and five eggs a day, depending on their egg-laying capacity. They can lay hundreds of eggs over the course of their lifetimes. The eggs, which are white and sticky when first laid, hatch in about a week at room temperature. Newly emerged bedbug nymphs are less than a pinhead, and they must feed regularly in order to grow into an adult.
While bedbugs are usually found on beds, they can also infest other furniture, including picture frames and electrical switch plates. They can even live in luggage and clothing. If you don’t want them to infest your possessions, you should use a bed bug exterminator to eliminate them from your home.