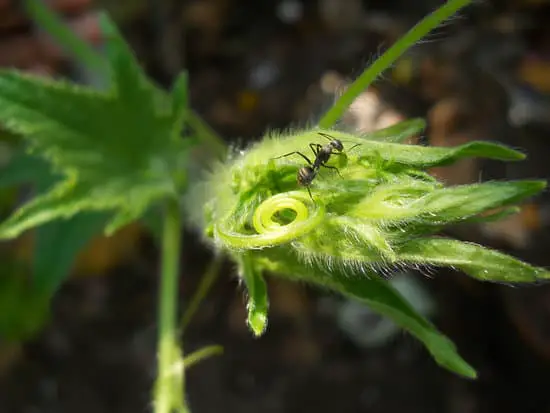
What Ants Are Polygynous?
Having multiple queens can have significant consequences on the colony’s life cycle. It may also lead to reproductive competition among queens. Besides, the kinship structure of nestmates may also be affected. Moreover, the sex ratio of offspring may also be affected.
Polygyny is observed in many species of pest ants. However, it is still unclear how these species are introduced and adapted to their new environments.
Polygynous colonies tend to be more adaptive than monogynous colonies. They are better suited for exploiting rapidly changing environments. These colonies may also fuse with other colonies to form polydomous colonies. Polydomous colonies can be connected by interchange of workers. They may also rear new queens from eggs.
Polygyne species exhibit complex social behavior. The number of queens, the number of nest sites, the growth rate of the colony, and the kinship structure of nestmates are all affected by the presence of multiple queens.
A polygynous colony may also have a higher recognition threshold than a monogynous colony. This may lead to more recognition errors. Moreover, it may also increase the probability of queen executions.
Polygyne ants also exhibit more complex behavior. One example is the ability of multiple queens to extend the invasion front. In the case of Argentine ants, a single colony may contain thousands of queens. Another example is the ability of opportunistic nesters to exploit short-lived nest sites.
Whether or not polygyne ants are a major threat to Taiwan is still unanswered. However, they may be a greater ecological threat to Taiwan than monogynous ants.