How Large Can Head Lice Get?
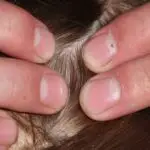
Head lice are small, 6-legged insects that live in the hair. They are grayish white, but can sometimes be red. Their eggs look like dandruff stuck to the hair. You can’t remove them with your fingers, but you can find them with a magnifying glass and a bright light.
To prevent the spread of head lice, it is best to avoid head-to-head contact. This means that your child should not share hats, clothing, towels, or even blankets with anyone. Also, it is best to wash all of your child’s personal items in hot water and dry them on high heat. If you must share your child’s clothing, be sure to wash it on a hot cycle and put it in a plastic bag to prevent further head-to-head contact. In addition, you can also soak hairbrushes in hot water to kill lice.
Adult head lice have six legs and are two to four mm long. They reproduce almost immediately and will lay eggs two days after mating. Adult lice live for about 35 days before dying. The life cycle of head lice is characterized by multiple molts. The first molt occurs two days after the egg is laid and the second occurs two days later. Lice cannot live in any other place, and they need to feed on human blood several times a day to stay alive.
The nymph stage of head lice is similar to that of an adult head louse. The nymph stage is the first stage in the life cycle, and it takes between nine and twelve days for the nymph to develop into an adult. Adult lice are slightly larger than nymphs, and the females are larger than males. Adult lice live on a person’s scalp for around 30 days, after which they fall off. They have hook-like claws at the end of their legs, and they are difficult to remove from hair shafts.