How Bed Bugs Turn Into Hives
Hives are the physical manifestation of an allergic reaction to something foreign to the skin. They are caused by an increased release of histamine by the immune system. The body’s response causes the skin to swell, and the inflammation causes a swelling of the tissue underneath the skin. The raised tissue, also known as urticaria, can be caused by many factors, including sunlight and pressure on the skin. While most hives disappear after a few days, chronic urticaria can last for weeks or months.
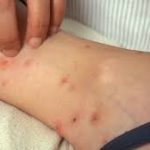
Hives can vary in color and size. Some are the same color as the skin itself, while others are darker red or purplish. The flat areas surrounding the hives may be inflamed. Hives look different from typical bed bug bites, which are usually round and evenly-edged. In addition, the skin around a hive may also be paler than the surrounding skin.
If you suspect that you have a bed bug infestation, a dermatologist can perform a diagnosis. He can also refer you to an allergist, who can test you for allergies. In addition to diagnosing the underlying allergy, an allergy specialist can prescribe antihistamines to alleviate your discomfort. A bed bug infestation can be difficult to spot, but a few red-brown specks of dung may suggest the presence of bed bugs.
While bed bug bites are not dangerous, they can affect your mental health. The itching and anticipation of additional bites may cause increased stress levels. However, despite these negative effects, most bites will heal on their own. Over-the-counter creams and home remedies can help treat bed bug bites, but it’s important to consult a doctor if they become infected.