Did You Know That Wasps Don’t Lose Stingers When They Attack?
Unlike the bees, wasps don’t lose stingers when they attack. They use them to protect their nest and prey. They also use them to transport prey back to their nest.
Wasp stings can be very painful and lead to a variety of complications. In the worst cases, the venom can cause an allergic reaction that can lead to anaphylactic shock, a severe allergic reaction that can be life threatening. In other cases, the venom can be a mild irritation that can be treated at home.
If you’re allergic to wasp stings, you need to get medical help. Some people have stronger reactions that may result in the loss of consciousness.
The first symptom to look for after a wasp sting is itching. This may only be local. Itching subsides within a few hours. However, if itching is persistent, you may want to seek medical attention.
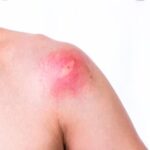
Besides itching, the main symptom is a red, swollen patch on your skin. You may also experience pupil dilation and muscle weakness. The swelling will usually go away within a few hours.
There are many different kinds of wasps and they vary in how they react to humans. They range from those that are aggressive to those that are less aggressive. A small minority of wasps are responsible for the bulk of human stings.
The general reaction to a wasp sting is usually intense itching and swelling. You might be able to feel a little dizzy after the sting. However, if you experience other symptoms such as shortness of breath or an increase in blood pressure, you should seek medical attention.