How Do Human Fleas Spread Diseases?
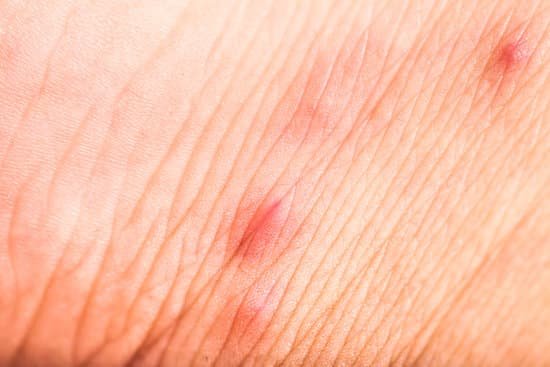
Human fleas can cause serious health problems, including infections and allergic reactions. They also carry bacteria that can lead to various health problems. While flea-borne disease cases are relatively infrequent in the United States, increased travel and rising temperatures may contribute to an increased risk of infection. One of the most common diseases transmitted by fleas is the bubonic plague. This disease was the cause of the “Black Death” epidemic of the fourteenth century, which killed an estimated 25 million people across Europe. Today, the disease is still present worldwide and can be transmitted by fleas that feed on rodents.
Although fleas prefer animals, humans are a good host for them. They can detect heat, movement, and vibrations from human skin to determine where to bite. Fleas can spread germs through feeding, as well as through their feces. In addition, the feces from a flea can infect an open wound.
Humans can contract plague by eating infected rodents, and there are many species of fleas that can transmit plague. These diseases are endemic in Europe, but the exact routes of transmission vary by country. In many countries, infection is spread through contact with an infected animal or by aerosols. In some countries, mosquitoes are also responsible for a significant portion of human infections.
Human fleas aren’t commonly found on humans, but they can infest other pets, including humans. The most common species in the United States is the cat flea, although dog fleas are also common.