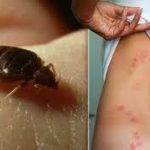
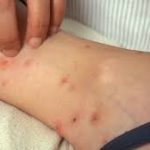
What Family Do Bed Bugs Belong To?
Bedbugs belong to a family of insects called Cimicidae. These insects feed on human blood and live inside human habitations. Their bite is diagnostic of an infestation. Bites are usually found on uncovered areas of the body, including the arms and legs. Young children are especially susceptible to bedbugs.
Bedbugs were once rare in the developed world, but a recent resurgence in their incidence has made the problem widespread. Increased travel and trade are thought to be two contributing factors. In addition to their prevalence in hotels, bedbugs are a serious problem in many private homes.
In addition to their bites, bedbugs emit a chemical signal, known as a pheromone, which protects them from being harassed by sexual predators. Bedbugs use this pheromone to communicate with one another. This pheromone may be used as a sexual cue by male bedbugs to avoid harassment from a sexual partner.
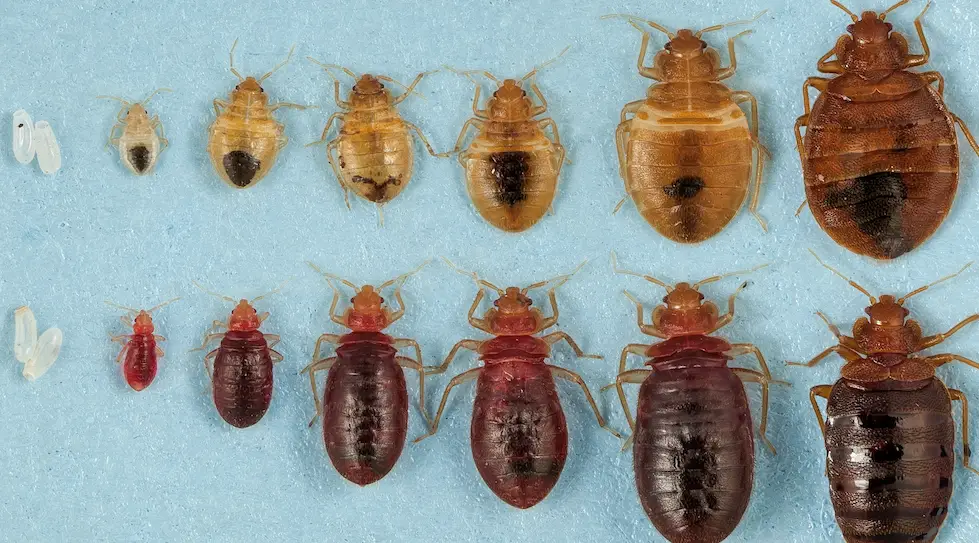
Bedbugs are closely related to the predatory minute pirate bugs and blood-feeding bat bugs. These bugs are found in warm environments, and are a common pest in homes and workplaces. The Cimicidae family includes two species of bedbugs, both of which are ectoparasites of humans. They range in size from 5 to 7 mm long. Their most common host is humans.
While many disease pathogens have been discovered in bed bugs, it is unclear if they can transmit them to humans. The most important thing to remember is that these bugs are hematophagous, which means they feed on blood. Their unique sexual behaviors make them unique among other arthropods. They also breed by traumatic insemination, which results in repeated exposure to pathogens and immune stimulation in the female. This shortens the lifespan of female bed bugs and could cause a natural selection in favor of those with active immune systems.