What Bed Bugs Do to Humans
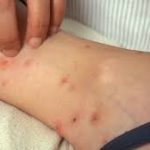
The itch and bites of bedbugs are uncomfortable and can result in severe allergic reactions. The itch may also be accompanied by a foul odor. However, bedbugs do not transmit any blood-borne diseases. Even though they are unpleasant, they can be treated with antiseptic soap and ice. Medications for pain relief may also be prescribed.
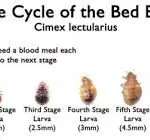
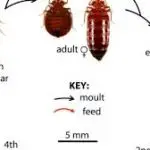
In order to feed, bedbugs pierce the skin with their mouth parts and inject a small amount of saliva into the host’s bloodstream. This saliva contains an anticoagulant and anesthetic properties that make the bite less painful. The bite is not noticeable until the skin reacts to the insect’s saliva, which may take anywhere from three to ten days. Only when the bedbugs reach maturity do they start reproducing. A female bedbug lays up to seven eggs a day, and hundreds throughout her life.
Some bedbug bites can cause serious infections, including Trypanosoma cruzi and Chagas disease. If left untreated, bedbugs can cause damage to the heart and central nervous system. People who have experienced these bites can be affected by anxiety and insomnia. Bedbugs can also affect the mental health of those who live in an infested home.
The bites from bedbugs are usually itchy and red. If left untreated, they may turn into blister-like inflammations. Fortunately, most bedbug bites heal on their own within a week or two. A corticosteroid cream can be applied to alleviate the itching and irritation.